| Keywords | Picture | >Key messages | Key publications | Research context |
| GRA:FITI | ![]() ![]() | Change the navigation of the UI of interest to optimize comparative evaluations! | Hammami et al., British HCI, 2017 | H. Hammami's PhD |
| States machines | ![]() ![]() | From explicit to implicit! Graph of tasks and behaviors to drive persuasion dynamically. | A. Fenicio's PhD | Easy Mountain |
| Pareto slider | ![]() ![]() | User's in the loop for understanding and mastering trade-offs in daily-life decisions about comfort. | Laurillau et al., Interact, 2021 | ANR INVOLVED |
| SEPIA | ![]() ![]() | Properties and functions to support the engineering of persuasive interaction. | Laurillau et al., EICS, 2016 | Orange Labs |
| Plasticy as a means for persuasion! | ![]() ![]() | For maintaining engagement of users in the behaviors change process over time, use plasticity to change the UI presentation! | Foulonneau et al., OzCHI, 2016 | Orange Labs |
| PDA-LPA | 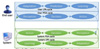 ![]() | First step towards a theory of adaptation! PDA-LPA is a design space grounded in the theory of psychological perception. It structures the adaptation life cycle into two regulation loops between the user and the system: a perception-decision-action (PDA) loop for both the system and the user, and a learning-prediction-adaptation (LPA) for supporting the adaptation, this last being particularly expressive for adaptivity. This PDA-LPA design space enables defining properties for assessing the quality of these loops between the system and the end-user. | Bouzit et al., RCIS, 2017 | Orange Labs |
| Evanescent adaptation | 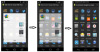 ![]() | Evanescent adaptation is a presentation of adaptation which ambition is two-fold: to speed up interaction when prediction is good; not to slow down interaction when prediction is wrong. | Bouzit et al., OzCHI, 2015 | Orange Labs |
| CRegrette | 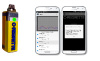 ![]() | Context is key! A persuasive system for smoking cessation | Fenicio and Calvary, AMI, 2015 | No funding |
| Style |  ![]() | From graphical user interfaces to robots: the need for plasticity! | Johal et al., CHI, 2014 | ANR MOCA |
| ARROW | 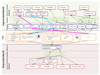 ![]() | Nine lessons from experience are reported about worth-centered design in practice. Worth maps appear as a treasure also for worth assessment over time, giving rise to the ARROW framework: Appreciations, Requirements and Rationale Of Worth. ARROWis refined into ARROWS (S for Support). | Camara and Calvary, Interact, 2015 and 2017 | F. Camara's PhD funded by Orange Labs Lannion as starting point |
| Quimera |  ![]() | Model-Driven Engineering supports the capacity of UIs to natively explain their design rationale. Quimera is a Quality Metamodel that makes it possible to justify any design decision explicitly. Thus, along a Model-Driven Engineering approach, the design rationale is alive at runtime and can be used for providing the end-users with context-sensitive explanations. | García Frey et al., EICS, 2011. | A. Garcia's PhD funded by the ITEA UsiXML european project |
| Compose |  ![]() | Context is key! Users's needs may appear opportunistically, making the task model dynamic. Whilst most approaches make the implicit hypothesis that the user's task model is static, Compose generates the task model dynamically from the specification of the user's needs (e.g., see a doctor). The algorithm is Planning-based, composing fragments of task models. | Garcia Frey et al., EICS, 2012. | Y. Gabillon's PhD funded by the Rhone-Alpes region |
| Magellan |  ![]() | Combine Model-Driven Engineering and genetic algorithms to support the exploration of the design space, and thereby inspire the designer. | Masson et al., EICS, 2010. | D. Masson's PhD |
| Plasticity as design principle |  ![]() | Considering plasticity at design time improves the quality of non-plastic UIs! | Serna et al., EICS, 2010. | A. Serna's Post doc, funded by the ANR MyCitizSpace and the ITEA UsiXML European projects. |
| Mega-UI |  ![]() | Empower users (designers and/or end-users) with Mega UIs rendering the graph of underlying models and metamodels. | Sottet et al., Springer HCI Series, 2007. | J.-S. Sottet's PhD |
| Models at runtime |  ![]() | Keep design models at runtime for implementing user interfaces plasticity as dynamic models transformations. | Sottet et al., Interact, 2007. | J.-S. Sottet's PhD |
| COMET |  ![]() | Use plastic widgets, i.e. widgets with multiple presentations capable of switching from one to another, for supporting native plasticity. | Demeure et al., DSVIS, 2008 | O. Daassi's and A. Demeure's PhDs |
| CAMELEON Reference Framework | 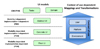 ![]() | Separation of concerns! Four levels of abstraction in design decisions in Human Computer Interaction, hypotheses about the context of use being step by step incorporated | Calvary et al., Interacting with Computers, 2003 | FP7 CAMELEON European project |













